Taking-off Measurements
Estimating costs for particular construction work can be divided into categories as follows.
Measurements are one of the most important parts in estimating the construction cost. Estimate the materials, labor, transport, or whatever the expenses are prior to the quantities gathered from the drawings. Therefore, quantities must be very accurate to estimate the construction cost.
Taking-off measurement is called the process of recording dimensions in a standard way which is accepted by construction professionals. It is done in a particular sheet called TDS. Taking-off measurements and estimating the project quantities are time-consuming, but it is required to be done. Because to reduce errors and give a rational elucidation for the estimated quantity whenever necessary. The measurements entered are should be accurate while being clear and readable for others.
- Method of construction
- Detail drawings
- Measurements
- Specification of materials
- Availability of material and market price
- Quantity (Labour and Material)
- Transport and operational expenses
Measurements are one of the most important parts in estimating the construction cost. Estimate the materials, labor, transport, or whatever the expenses are prior to the quantities gathered from the drawings. Therefore, quantities must be very accurate to estimate the construction cost.
Taking-off measurement is called the process of recording dimensions in a standard way which is accepted by construction professionals. It is done in a particular sheet called TDS. Taking-off measurements and estimating the project quantities are time-consuming, but it is required to be done. Because to reduce errors and give a rational elucidation for the estimated quantity whenever necessary. The measurements entered are should be accurate while being clear and readable for others.
In this article, we will discuss how we take measurements for excavation work for the foundation in a building.
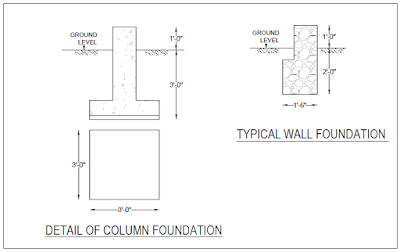 |
| Foundation Detail |
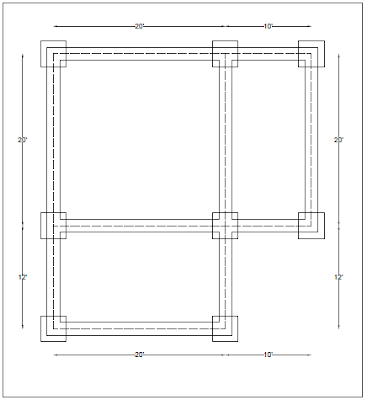 |
| Foundation Layout |
According to the given details in the drawings, we can find the centerline girth of the building.
Horizontal Lengths = 3 x 20’-0” + 2 x 10’-0”
= 60’=0” + 20’-0”
= 80’-0”
Vertical Lengths = 3 x 20’-0” + 2 x 12’-0”
= 60’-0” + 24’-0”
= 84’-0”
Centerline Girth = 80’-0” + 84’-0”
= 164’-0”
Let’s find the excavation volume of the rubble foundation with the following steps;
Excavation for Rubble Foundation = 164’-0” x 1’-6” x 2’-0”
= 492 Cu.ft
Ddt
For Column bases = 8 x 3’-0” x 3’-0” x 2’-0”
= (144 Cu.ft)
Therefore Total excavation for Rubble Foundation = 492 Cu.ft – 144 Cu.ft
= 348 Cu.ft
= 3.48 Cube
= 9.85 m3
Excavation for Column Bases = 8 x 3’-0” x 3’-0” x 3’-0”
= 216 Cu.ft
Total Excavation Work for the foundation of the Building = 348 Cu.ft + 216 Cu.ft
= 564 Cu.ft
= 5.64 Cube
= 15.96 m3